中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 128-140.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00070
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-03-31
修回日期:2025-05-13
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-11-26
作者简介:王伟军(1990—),男,甘肃酒泉人,博士,副教授,研究方向为乡村旅游与可持续生计、区域旅游发展。E-mail: wjwang@nwnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Weijun Wang1( ), Rong Lin1, Hua Li2, Juan Li1
), Rong Lin1, Hua Li2, Juan Li1
Received:2025-03-31
Revised:2025-05-13
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-26
摘要:
揭示旅游资源、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度的时空适配关系,是推动旅游业高质量发展的关键。以黄河流域69个市(州、盟)为研究对象,构建综合评价指标体系,融合多源数据,运用适配度模型、探索性空间数据分析和地理探测器等方法,分析2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配度的时空格局及驱动机制。结果表明:(1)2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源与旅游网络关注度整体呈波动上升趋势,而旅游经济水平则波动下降,区域差异显著。旅游资源禀赋高水平区由“孤岛化”向“组团化”演化,旅游经济持续呈多中心碎片化特征,旅游网络关注度维持中游>下游>上游的东高西低格局。(2)三者适配度总体上升,空间分布呈现东高西低的倒“T”形特征,并趋于集聚组团发展。(3)适配度空间集聚性减弱,表现出“东热西冷”的分布特征。(4)一般公共预算支出、进出口总额、R&D经费支出占GDP比重、PM2.5浓度、夜间灯光强度和植被覆盖率是影响适配度时空异质性的主要因素,且双因子交互作用显著,以增强效应为主。研究有助于识别“旅游资源诅咒”现象,为流域旅游业高质量发展提供理论支撑和政策参考。
中图分类号:
王伟军, 林蓉, 李花, 李娟. 黄河流域旅游资源-经济-网络关注度的时空适配格局及驱动机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(6): 128-140.
Weijun Wang, Rong Lin, Hua Li, Juan Li. Spatial-temporal pattern and driving mechanism of tourism resource-economy-network attention compatibility in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(6): 128-140.
| 目标层 | 指标层 | 单位 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 旅游资源禀赋指数 | A级景区数量 | 个 | 何昭丽等[ 赵书虹等[ 周成等[ |
| 国家级自然保护区数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级地质公园数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级森林公园数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级水利风景区数量 | 个 | ||
| 全国红色旅游经典景区数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家历史文化名村(镇)、传统部落数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级非物质文化遗产数量 | 个 | ||
| 世界遗产(文化类)数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家重点文物保护单位数量 | 个 | ||
| 旅游经济发展指数 | 旅游总收入 | 万元 | 杨宇民等[ 马勇等[ Yin等[ |
| 旅游总人次 | 万人 | ||
| 入境旅游人次 | 万人 | ||
| 旅游收入占第三产业GDP比重 | % | ||
| 星级酒店数 | 个 | ||
| 旅行社数量 | 个 | ||
| 旅游从业人数 | 万人 | ||
| 旅游网络关注度指数 | “城市+旅游”百度搜索指数 | 次 | 王琪林等[ |
表1 黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度评价指标体系
Table 1 Evaluation index system of tourism resource endowment, tourism economy and tourism network attention in Yellow River Basin
| 目标层 | 指标层 | 单位 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 旅游资源禀赋指数 | A级景区数量 | 个 | 何昭丽等[ 赵书虹等[ 周成等[ |
| 国家级自然保护区数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级地质公园数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级森林公园数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级水利风景区数量 | 个 | ||
| 全国红色旅游经典景区数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家历史文化名村(镇)、传统部落数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家级非物质文化遗产数量 | 个 | ||
| 世界遗产(文化类)数量 | 个 | ||
| 国家重点文物保护单位数量 | 个 | ||
| 旅游经济发展指数 | 旅游总收入 | 万元 | 杨宇民等[ 马勇等[ Yin等[ |
| 旅游总人次 | 万人 | ||
| 入境旅游人次 | 万人 | ||
| 旅游收入占第三产业GDP比重 | % | ||
| 星级酒店数 | 个 | ||
| 旅行社数量 | 个 | ||
| 旅游从业人数 | 万人 | ||
| 旅游网络关注度指数 | “城市+旅游”百度搜索指数 | 次 | 王琪林等[ |
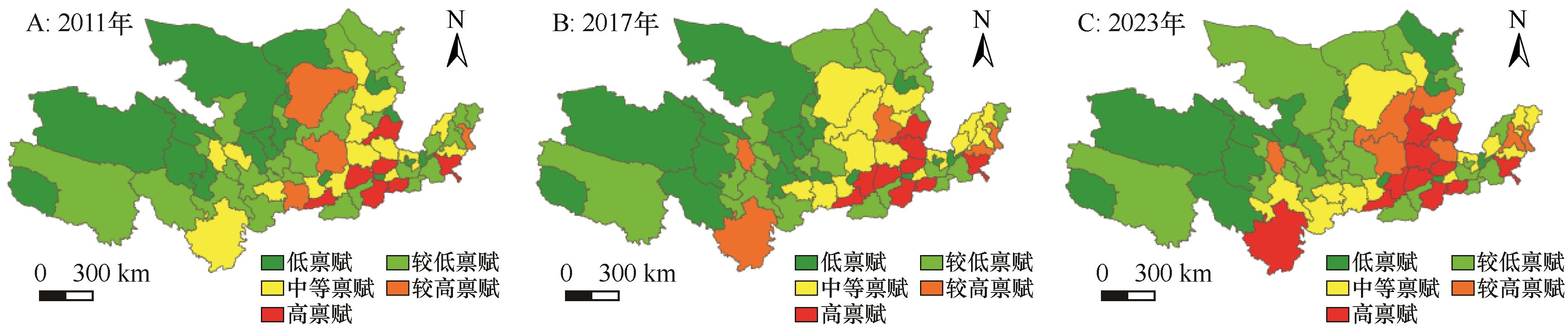
图3 黄河流域旅游资源禀赋的时空格局注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2019)1822号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.3 The spatiotemporal pattern of tourism resource endowment in the Yellow River Basin
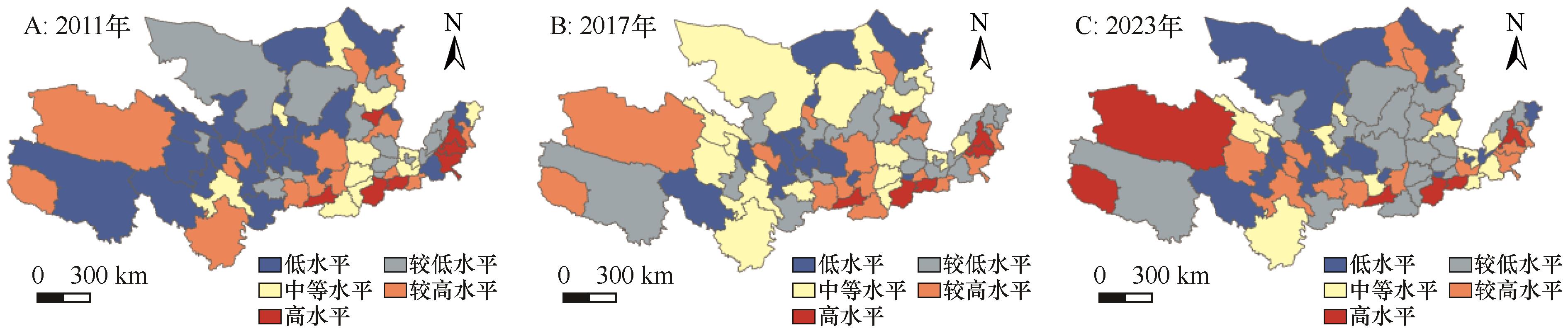
图5 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游经济发展时空分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2019)1822号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.5 The spatiotemporal pattern of tourism economic development in the Yellow River Basin
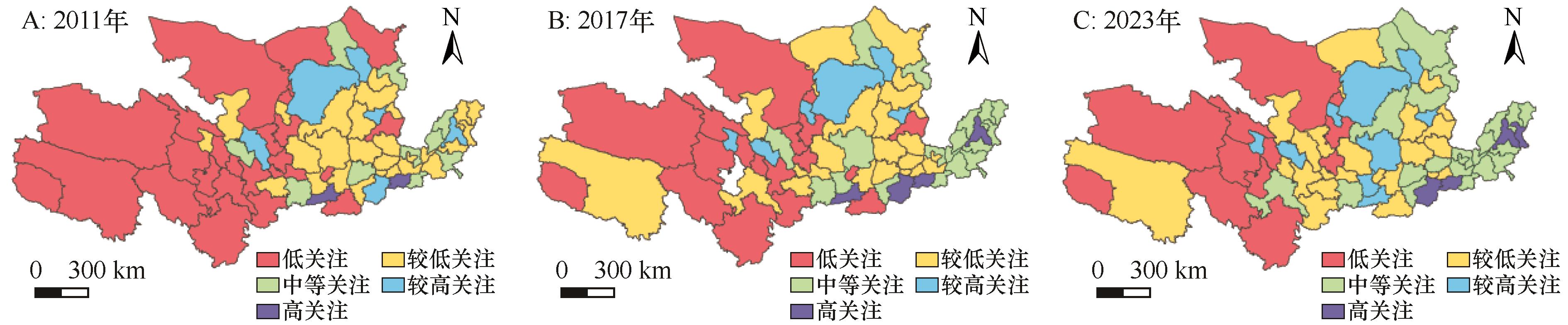
图7 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游网络关注度时空分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2019)1822号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.7 Spatiotemporal distribution of tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2023
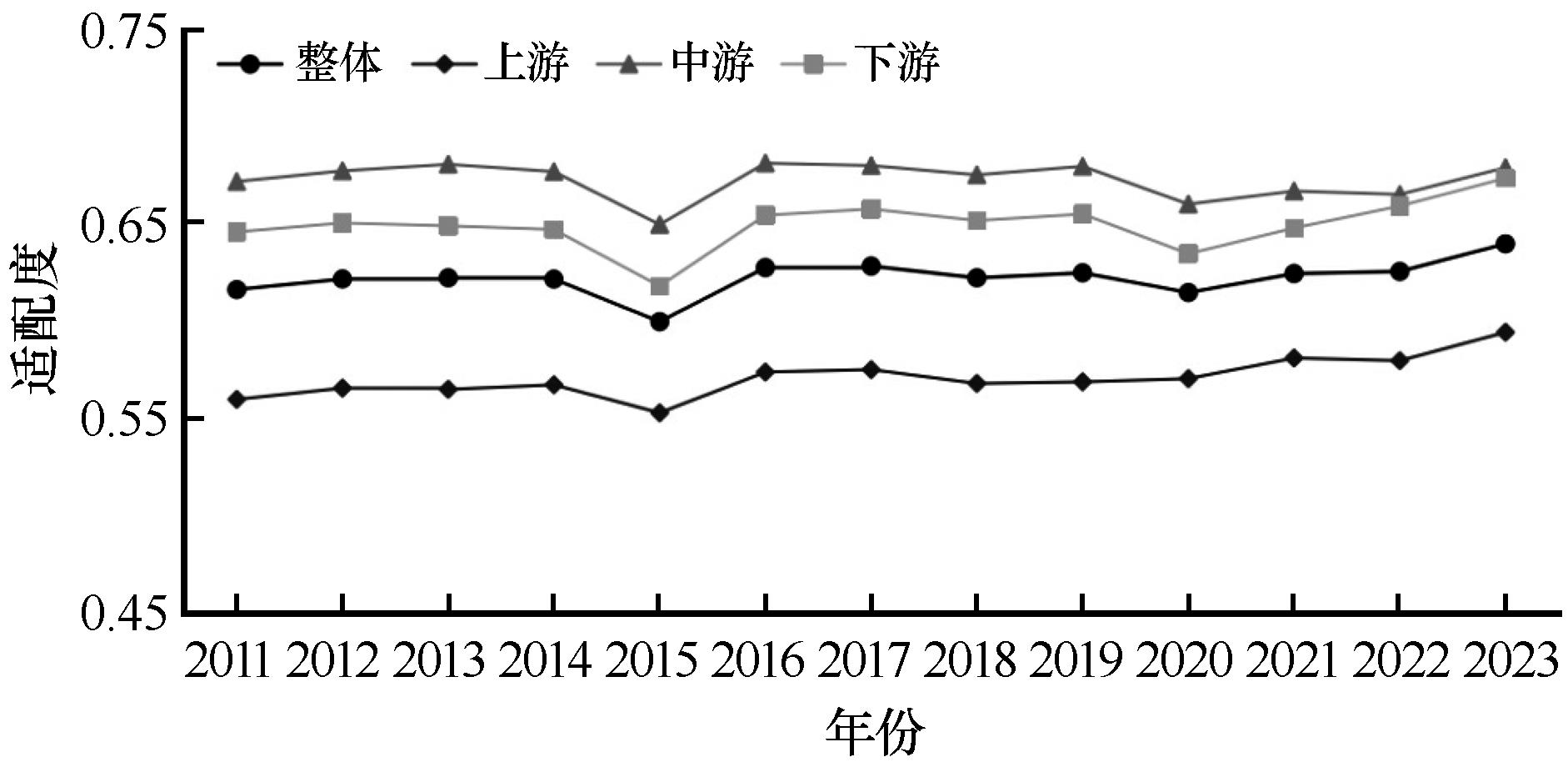
图8 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配度变化趋势
Fig.8 Trends of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2023
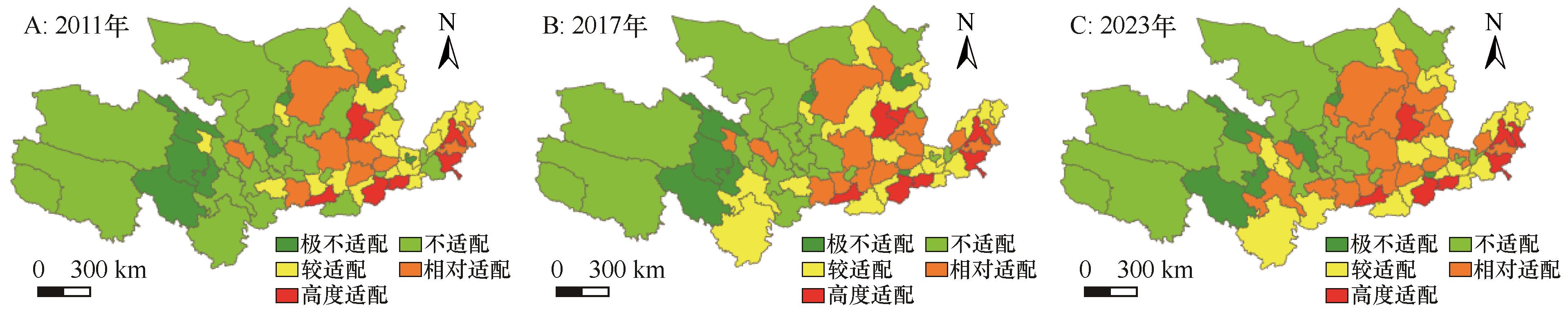
图9 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配度的空间分异注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2019)1822号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.9 Spatial differentiation of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2023
| 指标 | 年份 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Moran's I | 0.239 | 0.265 | 0.266 | 0.248 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.225 | 0.226 | 0.261 | 0.190 | 0.144 | 0.133 | 0.182 |
| Z | 3.976 | 4.371 | 4.391 | 4.115 | 3.303 | 3.959 | 3.741 | 3.758 | 4.298 | 3.230 | 2.482 | 2.314 | 3.050 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.002 |
表2 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配度的全局自相关指数
Table 2 The global autocorrelation index of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2023
| 指标 | 年份 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |
| Moran's I | 0.239 | 0.265 | 0.266 | 0.248 | 0.197 | 0.239 | 0.225 | 0.226 | 0.261 | 0.190 | 0.144 | 0.133 | 0.182 |
| Z | 3.976 | 4.371 | 4.391 | 4.115 | 3.303 | 3.959 | 3.741 | 3.758 | 4.298 | 3.230 | 2.482 | 2.314 | 3.050 |
| P | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.013 | 0.020 | 0.002 |
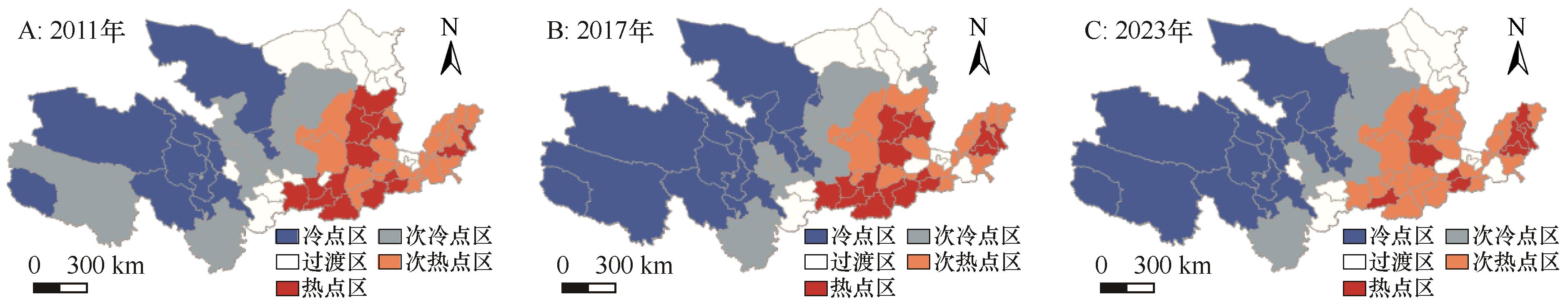
图10 2011—2023年黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配度的冷热点空间格局注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2019)1822号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.10 The hot/cold spot spatial pattern of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin from 2011 to 2023
| 指标类型 | 指标/单位 | 含义 | 编码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生态因素 | 年均气温/℃ | 自然条件 | X1 |
| 年降水量/m | X2 | ||
| 年均PM2.5浓度/(μg·m-3) | 城市的空气质量状况和变化趋势 | X3 | |
| 空气质量指数 | X4 | ||
| 植被覆盖率/% | 生态涵养潜力 | X5 | |
| 经济因素 | 人均GDP/元 | 地区经济实力状况 | X6 |
| 入境旅游收入占旅游总收入比重/% | 旅游对外开放程度 | X7 | |
| 进出口总额/万美元 | 城市开放程度 | X8 | |
| 第三产业占GDP比重/% | 产业结构 | X9 | |
| 常住人口城镇化率/% | 城镇化水平 | X10 | |
| 路网密度/km | 道路交通优势度 | X11 | |
| 社会因素 | 一般公共预算支出/万元 | 政府能力 | X12 |
| R&D经费支出占GDP比重/% | 科技素质教育 | X13 | |
| 政府工作报告中提及“旅游”及“文旅”等相关字样的次数/次 | 政策因素 | X14 | |
| 每万人拥有医疗机构床位数量/张 | 区域医疗保障设施 | X15 | |
| 每万人拥有公共交通车辆数量/辆 | 区域公共交通设施 | X16 | |
| 夜间灯光强度 | 城市规划、环境监测和经济发展水平 | X17 | |
| 生活垃圾无害化处理率/% | 生态环境净化力 | X18 | |
| 污水处理率/% | X19 | ||
| 人均(公园)绿地面积/m2 | 生态可持续修复力 | X20 |
表3 黄河流域旅游资源、经济与网络关注度适配度空间分异的影响因素选取
Table 3 The influencing factors of spatial differentiation of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin
| 指标类型 | 指标/单位 | 含义 | 编码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 生态因素 | 年均气温/℃ | 自然条件 | X1 |
| 年降水量/m | X2 | ||
| 年均PM2.5浓度/(μg·m-3) | 城市的空气质量状况和变化趋势 | X3 | |
| 空气质量指数 | X4 | ||
| 植被覆盖率/% | 生态涵养潜力 | X5 | |
| 经济因素 | 人均GDP/元 | 地区经济实力状况 | X6 |
| 入境旅游收入占旅游总收入比重/% | 旅游对外开放程度 | X7 | |
| 进出口总额/万美元 | 城市开放程度 | X8 | |
| 第三产业占GDP比重/% | 产业结构 | X9 | |
| 常住人口城镇化率/% | 城镇化水平 | X10 | |
| 路网密度/km | 道路交通优势度 | X11 | |
| 社会因素 | 一般公共预算支出/万元 | 政府能力 | X12 |
| R&D经费支出占GDP比重/% | 科技素质教育 | X13 | |
| 政府工作报告中提及“旅游”及“文旅”等相关字样的次数/次 | 政策因素 | X14 | |
| 每万人拥有医疗机构床位数量/张 | 区域医疗保障设施 | X15 | |
| 每万人拥有公共交通车辆数量/辆 | 区域公共交通设施 | X16 | |
| 夜间灯光强度 | 城市规划、环境监测和经济发展水平 | X17 | |
| 生活垃圾无害化处理率/% | 生态环境净化力 | X18 | |
| 污水处理率/% | X19 | ||
| 人均(公园)绿地面积/m2 | 生态可持续修复力 | X20 |
| 变量 | 2011年 | 2017年 | 2023年 | 均值 | 排序 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q值 | P值 | 排序 | q值 | P值 | 排序 | q值 | P值 | 排序 | |||||
| X1 | 0.280 | 0.006 | 11 | 0.275 | 0.007 | 11 | 0.327 | 0.748 | 5 | 0.294 | 7 | ||
| X2 | 0.304 | 0.404 | 9 | 0.179 | 0.999 | 17 | 0.248 | 0.074 | 13 | 0.244 | 14 | ||
| X3 | 0.375 | 0.001 | 3 | 0.317 | 0.683 | 7 | 0.347 | 0.850 | 3 | 0.346 | 4 | ||
| X4 | 0.172 | 1.000 | 20 | 0.385 | 0.000 | 4 | 0.309 | 0.549 | 8 | 0.288 | 10 | ||
| X5 | 0.316 | 0.006 | 8 | 0.294 | 0.013 | 9 | 0.282 | 0.029 | 9 | 0.297 | 6 | ||
| X6 | 0.179 | 0.998 | 19 | 0.157 | 0.938 | 18 | 0.238 | 0.075 | 14 | 0.191 | 18 | ||
| X7 | 0.231 | 0.044 | 14 | 0.206 | 0.114 | 16 | 0.201 | 0.088 | 17 | 0.213 | 17 | ||
| X8 | 0.488 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.412 | 0.707 | 3 | 0.377 | 0.002 | 2 | 0.426 | 2 | ||
| X9 | 0.222 | 0.981 | 16 | 0.251 | 0.953 | 13 | 0.207 | 0.970 | 16 | 0.227 | 16 | ||
| X10 | 0.294 | 0.698 | 10 | 0.293 | 0.027 | 10 | 0.249 | 0.004 | 12 | 0.279 | 11 | ||
| X11 | 0.337 | 0.008 | 7 | 0.273 | 0.014 | 12 | 0.262 | 0.954 | 11 | 0.291 | 9 | ||
| X12 | 0.729 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.710 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.733 | 0.013 | 1 | 0.724 | 1 | ||
| X13 | 0.363 | 0.002 | 5 | 0.426 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.312 | 0.012 | 7 | 0.367 | 3 | ||
| X14 | 0.194 | 0.160 | 18 | 0.074 | 0.798 | 20 | 0.072 | 1.000 | 20 | 0.113 | 20 | ||
| X15 | 0.247 | 0.039 | 12 | 0.358 | 0.920 | 5 | 0.222 | 1.000 | 15 | 0.276 | 12 | ||
| X16 | 0.338 | 0.968 | 6 | 0.226 | 0.026 | 15 | 0.200 | 0.161 | 18 | 0.255 | 13 | ||
| X17 | 0.364 | 0.189 | 4 | 0.331 | 0.036 | 6 | 0.341 | 0.097 | 4 | 0.345 | 5 | ||
| X18 | 0.235 | 0.094 | 13 | 0.315 | 0.892 | 8 | 0.326 | 0.561 | 6 | 0.292 | 8 | ||
| X19 | 0.229 | 0.978 | 15 | 0.156 | 0.158 | 19 | 0.180 | 0.405 | 19 | 0.188 | 19 | ||
| X20 | 0.213 | 0.052 | 17 | 0.236 | 0.081 | 14 | 0.276 | 0.371 | 10 | 0.241 | 15 | ||
表4 黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济与旅游网络关注度适配影响因素的地理探测结果
Table 4 Geographical exploration results of influencing factors of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin
| 变量 | 2011年 | 2017年 | 2023年 | 均值 | 排序 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| q值 | P值 | 排序 | q值 | P值 | 排序 | q值 | P值 | 排序 | |||||
| X1 | 0.280 | 0.006 | 11 | 0.275 | 0.007 | 11 | 0.327 | 0.748 | 5 | 0.294 | 7 | ||
| X2 | 0.304 | 0.404 | 9 | 0.179 | 0.999 | 17 | 0.248 | 0.074 | 13 | 0.244 | 14 | ||
| X3 | 0.375 | 0.001 | 3 | 0.317 | 0.683 | 7 | 0.347 | 0.850 | 3 | 0.346 | 4 | ||
| X4 | 0.172 | 1.000 | 20 | 0.385 | 0.000 | 4 | 0.309 | 0.549 | 8 | 0.288 | 10 | ||
| X5 | 0.316 | 0.006 | 8 | 0.294 | 0.013 | 9 | 0.282 | 0.029 | 9 | 0.297 | 6 | ||
| X6 | 0.179 | 0.998 | 19 | 0.157 | 0.938 | 18 | 0.238 | 0.075 | 14 | 0.191 | 18 | ||
| X7 | 0.231 | 0.044 | 14 | 0.206 | 0.114 | 16 | 0.201 | 0.088 | 17 | 0.213 | 17 | ||
| X8 | 0.488 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.412 | 0.707 | 3 | 0.377 | 0.002 | 2 | 0.426 | 2 | ||
| X9 | 0.222 | 0.981 | 16 | 0.251 | 0.953 | 13 | 0.207 | 0.970 | 16 | 0.227 | 16 | ||
| X10 | 0.294 | 0.698 | 10 | 0.293 | 0.027 | 10 | 0.249 | 0.004 | 12 | 0.279 | 11 | ||
| X11 | 0.337 | 0.008 | 7 | 0.273 | 0.014 | 12 | 0.262 | 0.954 | 11 | 0.291 | 9 | ||
| X12 | 0.729 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.710 | 0.001 | 1 | 0.733 | 0.013 | 1 | 0.724 | 1 | ||
| X13 | 0.363 | 0.002 | 5 | 0.426 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.312 | 0.012 | 7 | 0.367 | 3 | ||
| X14 | 0.194 | 0.160 | 18 | 0.074 | 0.798 | 20 | 0.072 | 1.000 | 20 | 0.113 | 20 | ||
| X15 | 0.247 | 0.039 | 12 | 0.358 | 0.920 | 5 | 0.222 | 1.000 | 15 | 0.276 | 12 | ||
| X16 | 0.338 | 0.968 | 6 | 0.226 | 0.026 | 15 | 0.200 | 0.161 | 18 | 0.255 | 13 | ||
| X17 | 0.364 | 0.189 | 4 | 0.331 | 0.036 | 6 | 0.341 | 0.097 | 4 | 0.345 | 5 | ||
| X18 | 0.235 | 0.094 | 13 | 0.315 | 0.892 | 8 | 0.326 | 0.561 | 6 | 0.292 | 8 | ||
| X19 | 0.229 | 0.978 | 15 | 0.156 | 0.158 | 19 | 0.180 | 0.405 | 19 | 0.188 | 19 | ||
| X20 | 0.213 | 0.052 | 17 | 0.236 | 0.081 | 14 | 0.276 | 0.371 | 10 | 0.241 | 15 | ||

图12 黄河流域旅游资源禀赋、旅游经济、旅游网络关注度适配度的驱动机制
Fig.12 The driving mechanism of compatibility among tourism resource endowment, tourism economy, and tourism network attention in the Yellow River Basin
| [1] | Adu-Ampong E A.Tourism and national economic development planning in Ghana,1964-2014[J].International Development Planning Review,2018,40(1):75-95. |
| [2] | Yin Z, Tang Y, Liu H,et al.Coupling coordination relationship between tourism economy-social welfare-ecological environment:empirical analysis of western area,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2023,155:110938. |
| [3] | 罗浩,颜钰荛,杨旸.中国各省的旅游增长方式“因地制宜”吗?:中国省际旅游增长要素贡献与旅游资源比较优势研究[J].旅游学刊,2016,31(3):43-53. |
| [4] | Denicolai S, Cioccarelli G, Zucchella A.Resource-based local development and networked core-competencies for tourism excellence[J].Tourism Management,2010,31:260-266. |
| [5] | 张洪,时浩楠.安徽省旅游资源与旅游经济的空间错位研究[J].地域研究与开发,2015,34(4):80-83. |
| [6] | 戴镇涛,尹琴,陈叙成.云南省旅游景区丰度与网络关注度的空间错位[J].四川师范大学学报(自然科学版),2024,47(5):631-637. |
| [7] | 王琪林,杨霞,方怡.四川省旅游资源丰裕度与旅游网络关注度空间错位演变及影响因素分析[J].旅游科学,2023,37(1):43-58. |
| [8] | 马丽君,郭留留,吴志才.“爸爸去哪儿”对拍摄地旅游发展的影响:基于游客网络关注度的分析[J].旅游科学,2016,30(3):57-68. |
| [9] | 张嫚,黄凌云.负面网络关注度对旅游业发展的影响:基于旅游需求的空间关联分析[J].旅游学刊,2021,36(7):81-91. |
| [10] | Ge Q, Yang J, Wang Y.Dynamic coupled coordination and spatial correlation between ice-snow tourism network attention and tourism industry development systems:evidence from 31 provinces of China[J].Research in Cold and Arid Regions,2024,16(5):259-267. |
| [11] | 杨宇民,焦胜,廖婧茹,等.人口规模与交通环境影响的中国城市旅游资源-经济空间错位[J].经济地理,2021,41(1):221-231. |
| [12] | 李梦龙,柯月嫦,吴映梅.云南省旅游资源和旅游经济错位特征及优化[J].云南地理环境研究,2023,35(2):53-60. |
| [13] | 黄远水,赵黎明.风景名胜区旅游竞争力的构成和来源[J].旅游学刊,2005,20(5):62-66. |
| [14] | 庞闻,马耀峰,李丹.中国省域旅游经济与可持续发展耦合关系和影响因素研究[J].人文地理,2024,39(5):167-175. |
| [15] | 唐承财,王希羽,韩莹,等.黑龙江省中俄边境城市旅游网络关注度时空特征及影响因素[J].中国生态旅游,2024,14(5):1118-1128. |
| [16] | 何昭丽,王松茂.中国旅游资源转换效率的时空演变及影响机理[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2020,30(11):185-193. |
| [17] | 赵书虹,白梦,阮梦枝,等.云南省旅游资源与生态安全协调发展的时空演化特征及障碍因子分析[J].地理科学,2021,41(3):493-503. |
| [18] | 周成,柳炳华,张旭红,等.黄河流域文物保护单位空间分布特征及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(6):10-20. |
| [19] | 马勇,李丽霞,任洁.神农架林区旅游经济-交通状况-生态环境协调发展研究[J].经济地理,2017,37(10):215-220. |
| [20] | 孙涵,聂飞飞,胡雪原.基于熵权TOPSIS法的中国区域能源安全评价及差异分析[J].资源科学,2018,40(3):477-485. |
| [21] | 吉宇琴,姜会明.新时代老龄化与养老资源适配度时空差异及其影响因素分析[J].地理科学,2022,42(5):851-862. |
| [22] | 麻学锋,孙洋.旅游产业发展与民生福祉适配关系研究:以张家界为例[J].旅游科学,2024,38(6):1-19. |
| [23] | 王兆峰,张先甜.中国人-地-粮复合系统适配性评价及影响[J].地理学报,2024,79(3):779-799. |
| [24] | 赵雪雁,王伟军,万文玉.中国居民健康水平的区域差异:2003-2013[J].地理学报,2017,72(4):685-698. |
| [25] | 王劲峰,徐成东.地理探测器:原理与展望[J].地理学报,2017,72(1):116-134. |
| [26] | 王新越,郭利贞.中国旅游经济适应性循环演化及影响机理[J].地理科学,2024,44(2):297-308. |
| [27] | 薛明月,王成新,赵金丽,等.黄河流域旅游经济空间分异格局及影响因素[J].经济地理,2020,40(4):19-27. |
| [28] | 周成,张旭红,张倩,等.黄河流域“五位一体”综合评价体系建构与空间差异研究[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):1-11. |
| [29] | Li X, Huang S, Song C.China's outward foreign direct investment in tourism[J].Tourism Management,2017,59:1-6. |
| [30] | 徐冬,黄震方,黄睿.基于空间面板计量模型的雾霾对中国城市旅游流影响的空间效应[J].地理学报,2019,74(4):814-830. |
| [31] | 解智涵,刘敏,闫旭纲.山西重要地质遗迹空间分布特征及旅游响应[J].地理研究,2024,43(7):1809-1826. |
| [1] | 刘迪, 马安奇, 李凤鸣, 陈海, 桂伊晴. 黄河流域居民福祉时空格局及其驱动因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 102-112. |
| [2] | 李光勤, 李佳欣, 郭细根. 黄河流域绿色创新与绿色金融耦合协调的时空演化及区域差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 113-123. |
| [3] | 苏孜, 周德良, 李浩. 数字经济对黄河流域产业结构转型升级的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 161-171. |
| [4] | 陈锋, 曲相昱. 黄河流域中游省区自然-社会系统可持续发展安全公正空间测度[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 194-208. |
| [5] | 刘建华, 高新科, 葛世帅, 施天乐. 黄河流域数字经济发展与能源利用效率的关联特征及作用机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 338-349. |
| [6] | 柳江, 李艳吉. 数字新基建赋能黄河流域高质量发展:机制与空间溢出[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 369-379. |
| [7] | 王昱, 袁兴鹏, 李浩霖, 张英, 苗天, 田苗, 信雅玲, 胡飞燕. 黄河甘肃段上游及洮河大型底栖动物群落结构特征及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 284-293. |
| [8] | 徐雪, 王永瑜. 基于双重逻辑视角的黄河流域城乡融合发展评价及空间差异分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 1-13. |
| [9] | 李光勤, 牛雯琦, 王江姣. 黄河流域农业面源污染的演化特征与区域差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 146-154. |
| [10] | 苏耀华, 赵鹏睿, 柳江. 黄河流域数字经济与制造业高质量发展耦合协调及其障碍因子[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 268-276. |
| [11] | 冀雪霜, 孙鹏. 黄河流域生态足迹演进、时空分异与驱动因素——兼论环境库兹涅茨曲线的空间效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 58-69. |
| [12] | 邱娟, 陈钦萍, 王波, 刘振滨. 黄河流域技术创新与农业绿色高质量发展耦合协调及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 275-283. |
| [13] | 杨华庆, 朱睿, 尹振良, 山建安, 张薇, 方春爽. 2001—2020年黄河流域水源涵养区植被覆盖变化及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 57-70. |
| [14] | 张明斗, 杨雨欣. 黄河流域城市产业结构生态化的时空格局及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 108-118. |
| [15] | 解智涵, 刘敏, 闫旭纲, 任亚鹏. 黄河流域重要地质遗迹空间格局及地质旅游开发潜力评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 128-139. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
